1970061—ERKM—Final V1.0
1970061—ERKM—Final V1.0
- 74 pages
- For Official Use Only
- April 30, 2004
The mission of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is to uphold the law through the investigation of violations of federal criminal law; to protect the United States from foreign intelligence and terrorist activities; and to provide leadership and law enforcement assistance to federal, state, local and international agencies. Vital to the support of the FBI mission is the implementation of records management policies and procedures that ensure the proper creation, maintenance, use and disposition of records.
The FBI, like all other Federal agencies, is required by statute to “make and preserve records
containing adequate and proper documentation of the organization, functions, policies, decisions,
procedures, and essential transactions of the agency.”1 This practice of ensuring “adequate and
proper documentation”2 is essential to efficient and economical agency operations by
guaranteeing that information is documented in official files, including electronic recordkeeping
(ERK) systems, where it will be accessible to all authorized staff that may need it.
As the FBI evolves from paper-intensive records and information management systems to more
electronic, paperless records and information management systems, electronic information
systems (IS) containing records must comply with the policies and procedures governing the
management of FBI records.The Assistant Director of the Records Management Division (RMD) is the FBI Records Officer
(RO). On April 29, 2002, the Director of the FBI delegated to the Records Officer the authority
to determine what FBI information constitutes a record under Federal Law and the authority to
approve, or withhold approval of, any electronic information or knowledge management (KM)
system in use or under production. 3 No electronic information or knowledge management
system is to be utilized in the conduct of FBI business without the approval of the FBI RO.
The RO’s highest priority is to ensure that support for records management criteria is
incorporated into requirements specifications and test plans of new information and knowledge
management systems. The second highest priority is to review existing systems within the FBI
to ensure compliance. Development efforts may continue on new information systems; however,
it is incumbent on the Project Manager of any information or knowledge management system in
development to ensure coordination with the Records Officer, as the system may not become
operational absent RO authorization. To this end, the FBI created the Electronic Recordkeeping
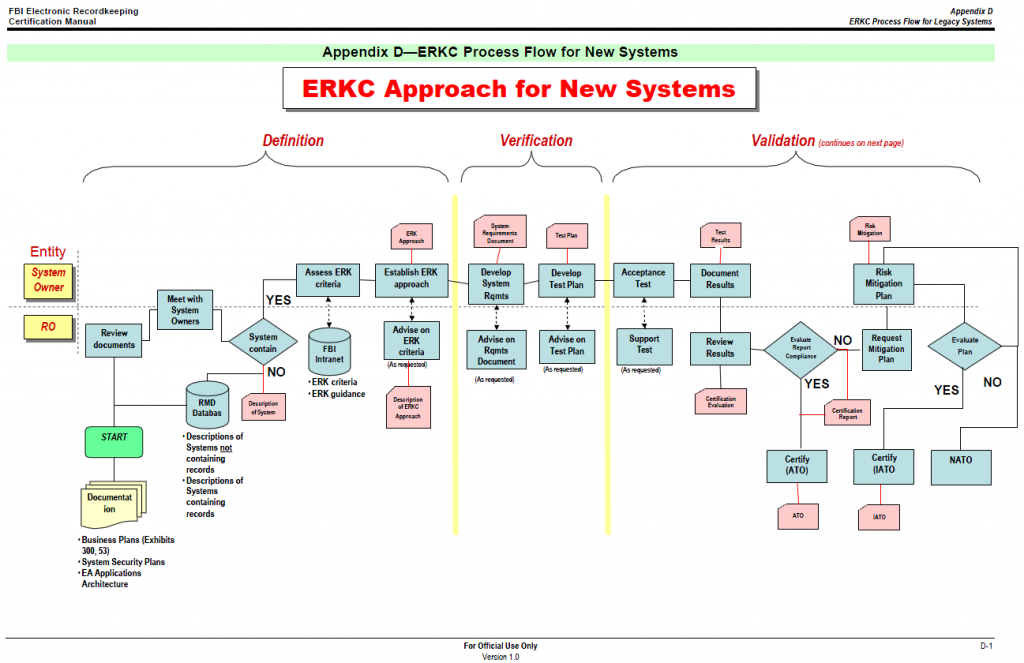
Certification (ERKC) process as described in this manual.Implementation of the ERKC process ensures that the systems the FBI develops and maintains
comply with statutory and agency electronic recordkeeping requirements. The ERKC process
incorporates electronic recordkeeping requirements into the system development life cycle (SDLC) so that all system development activities can appropriately consider electronic
recordkeeping issues from the earliest stages of acquisition and design.The ERKC is a process used to evaluate system compliance with records management criteria.
The process is designed to guide system sponsors and developers in assessing and incorporating
records management criteria into system requirements specifications, and then ensuring
fulfillment through review of documented test results. The ERKC process consists of identifying
systems that contain records, helping System Owners and developers understand ERK criteria,
ensuring that system requirements specifications satisfy ERK criteria, and validating ERK
functionality through review of system test results.Forming partnerships with other information professionals is essential. The ERKC process is
designed to leverage the outputs from existing IT systems management processes to minimize
redundant data capture and reduce the burden on systems development and management
activities.…
1.4 Electronic Recordkeeping Certification (ERKC)
The Electronic Recordkeeping Certification (ERKC) process described in this manual is the
FBI’s official process to comprehensively evaluate the technical and non-technical electronic
records management features of FBI information systems and to determine whether they satisfy
the ERK compliance criteria. The certification determination can take one of the following
forms:§ Approval to Operate (ATO)—approval to operate a system because it meets all recordkeeping
criteria (ATOs must be recertified every three years),§ Interim Approval to Operate (IATO)—temporary approval to operate a system for a defined
period of time and under certain defined conditions, or§ No Approval to Operate (NATO)—denial of approval to operate a system because it fails to
meet recordkeeping criteria.In addition, the ERKC process provides standardized methods of evaluating a system for ERK
compliance and recognizes four architectural approaches to achieving such compliance:§ Integration—an approach based on integrating a Department of Defense (DoD) 5015.2-
certified Records Management Application (RMA) with the information system for which
certification is sought.§ Direct Export—an approach based on incorporating the necessary features within the
information system for which certification is sought such that the system is able to automatically
export Federal records and their associated metadata to an existing shared FBI
RMA. (Virtual Case File will include an RMA in its architecture, so exporting records to
it is a recognized option.)§ Integral—an approach based on designing and building an information system such that it
performs all of the necessary ERK functions internal to the system itself.§ Deferred—an approach intended to permit temporary certification for information systems
that are designed and built for specific purposes in response to tactical or emergency
situations (e.g., response to the D.C. sniper investigations). Once the emergency situation
is over, owners of such systems must determine whether to (1) dispose of the system and
transfer all appropriate records to an approved RMA or (2) request certification for the
system if it will have recurring use in the future.…