The following report was released July 15, 2013 by the Department of Homeland Security’s Office of Intelligence and Analysis.
2012 National Network of Fusion Centers Final Report
- 105 pages
- June 2013
Threats to the homeland are persistent and constantly evolving. Domestic and foreign terrorism and the expanding reach of transnational organized crime syndicates across cyberspace, international borders, and jurisdictional boundaries within the United States highlight the continued need to build and sustain effective intelligence and information sharing partnerships among the federal government; state, local, tribal, and territorial (SLTT) governments; and the private sector. These partnerships are the foundation of a robust and efficient homeland security intelligence enterprise that goes beyond shared access to information and intelligence to foster sustained collaboration in support of a common mission. This collaboration enables the fusion process and provides decision makers across all levels of government and within the private sector with the knowledge to make informed decisions to protect the homeland from a variety of threats and hazards.
State and major urban area fusion centers (fusion centers) are the nexus of the homeland security intelligence enterprise at the state and local level. They serve as focal points for the receipt, analysis, gathering, sharing, and safeguarding of threat-related information between the federal government and SLTT and private sector partners. As such, fusion centers provide a state and local context that enhances the national threat picture and enables local officials to better protect their communities. They also provide critical information and subject matter expertise that allows the Intelligence Community (IC) to more effectively “connect the dots” to prevent and protect against threats to the homeland.
Background
Beginning in 2003, the federal government cooperated with state and local entities to develop and publish guidance to enable individual fusion centers to operate at a baseline level of capability and to form a robust and fully integrated National Network of Fusion Centers (National Network). To successfully perform these functions, fusion centers must develop and mature capabilities that enable efficient and effective information sharing, safeguarding, and analysis across the National Network and the broader Homeland Security Enterprise (HSE). To guide the development of fusion center capabilities, Fusion Center Directors and the federal government jointly identified four Critical Operational Capabilities (COCs), which together reflect the operational priorities of the National Network, and four Enabling Capabilities (ECs), which provide a foundation for the fusion process.
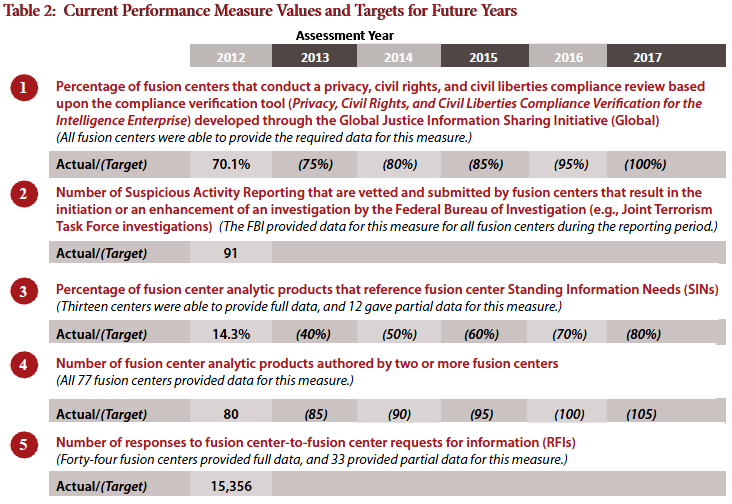
In 2011, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s (DHS) Office of Intelligence and Analysis (I&A), in coordination with federal and SLTT partners, began conducting an annual assessment of fusion centers to evaluate their progress in achieving the COCs and ECs and to collect additional data to better understand the characteristics of individual fusion centers and the National Network as a whole. DHS/I&A initiated the 2012 Fusion Center Assessment (2012 Assessment) in August 2012 as the second iteration of the annual assessment process and the first assessment to provide data on year-over-year progress in implementing the COCs and ECs. The 2012 Assessment was also the first assessment to collect National Network performance data based on an initial set of five performance measures adopted in 2011.
This 2012 National Network of Fusion Centers Final Report (2012 Final Report) summarizes and characterizes the overall capabilities and performance of the National Network based on the results of the 2012 Assessment. This report does not include fusion center-specific capability or performance data. Instead, it uses aggregated data from the 2012 Assessment to describe the capability and performance achievements of the National Network.
This report also outlines ongoing efforts by National Network stakeholders to implement an outcome-based performance management framework to better understand the value and impact of the National Network in supporting national information sharing and homeland security outcomes.
…